Understanding Autoimmune Disorders in Ayurveda: A Holistic Perspective
What Are Autoimmune Disorders?
Rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, multiple sclerosis, and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis are just a few of the many illnesses that fall under the umbrella of autoimmune disorders. Frequently, a mix of lifestyle, environmental, and hereditary variables is the root cause.
The Ayurvedic Viewpoint
According to Ayurveda, the equilibrium of the three doshas—Pitta, Kapha, and Vata—defines health. Generally speaking, autoimmune diseases signify a disturbance in this equilibrium, which is frequently connected to the buildup of toxins (ama) and an imbalance in the body’s energy.
Key Concepts in Ayurveda Related to Autoimmune Disorders:
- Agni (Digestive Fire): Good health depends on a robust digestive fire. Ama can develop as a result of poor digestion, and this can exacerbate autoimmune diseases.
- Dosha Imbalance: An excess of Vata, which causes dryness and instability, or Pitta, which causes inflammation and heat, are common in autoimmune illnesses.
- Sattva, Rajas, and Tamas: The three gunas (qualities) of sattva, rajas, and tamas have an impact on mental and emotional health. An imbalance can lead to stress, which makes autoimmune diseases worse.
Samprapti according to ayurveda:

The term “Samprapti” in Ayurveda describes the pathophysiology or course of an illness. By emphasizing the interaction of doshas (body energies), dhatus (tissues), and the impact of other circumstances, this paradigm helps explain autoimmune disorders. According to Ayurvedic principles, the following is a condensed summary of the symptoms of autoimmune diseases:
- Dosha Imbalance: An imbalance between the doshas of Vata, Pitta, and Kapha is frequently the initial cause of autoimmune disorders. A poor diet, poor lifestyle choices, stress, or environmental factors can all contribute to this imbalance.
- Disruption of Srotas (Channels): A dosha imbalance may result in obstructions or malfunctions in the body’s srotas, which can impact the removal of toxins and the passage of nutrients.
- Ama Formation: Toxic byproducts known as ama can occur as a result of poor digestion (Agni). Ama may build up in the body, interfere with regular physiological processes, and even target healthy tissues.
- The immune system may unintentionally attack the body’s own tissues, resulting in dhatukshaya (depletion of the body tissues), which can cause discomfort and malfunction in a number of systems.
- Different doshas may become dominant in vata-pitta-kapha dysregulation, which can lead to distinct symptoms depending on the autoimmune illness. As an example, lupus may exhibit more Pitta traits, whereas rheumatoid arthritis may entail more Vata and Kapha.
- Psychological Factors: According to Ayurveda, emotional stress and mental health are important since they may exacerbate dosha imbalances and accelerate the course of disease.
- Chikitsa (Treatment): To promote general health and immunity,
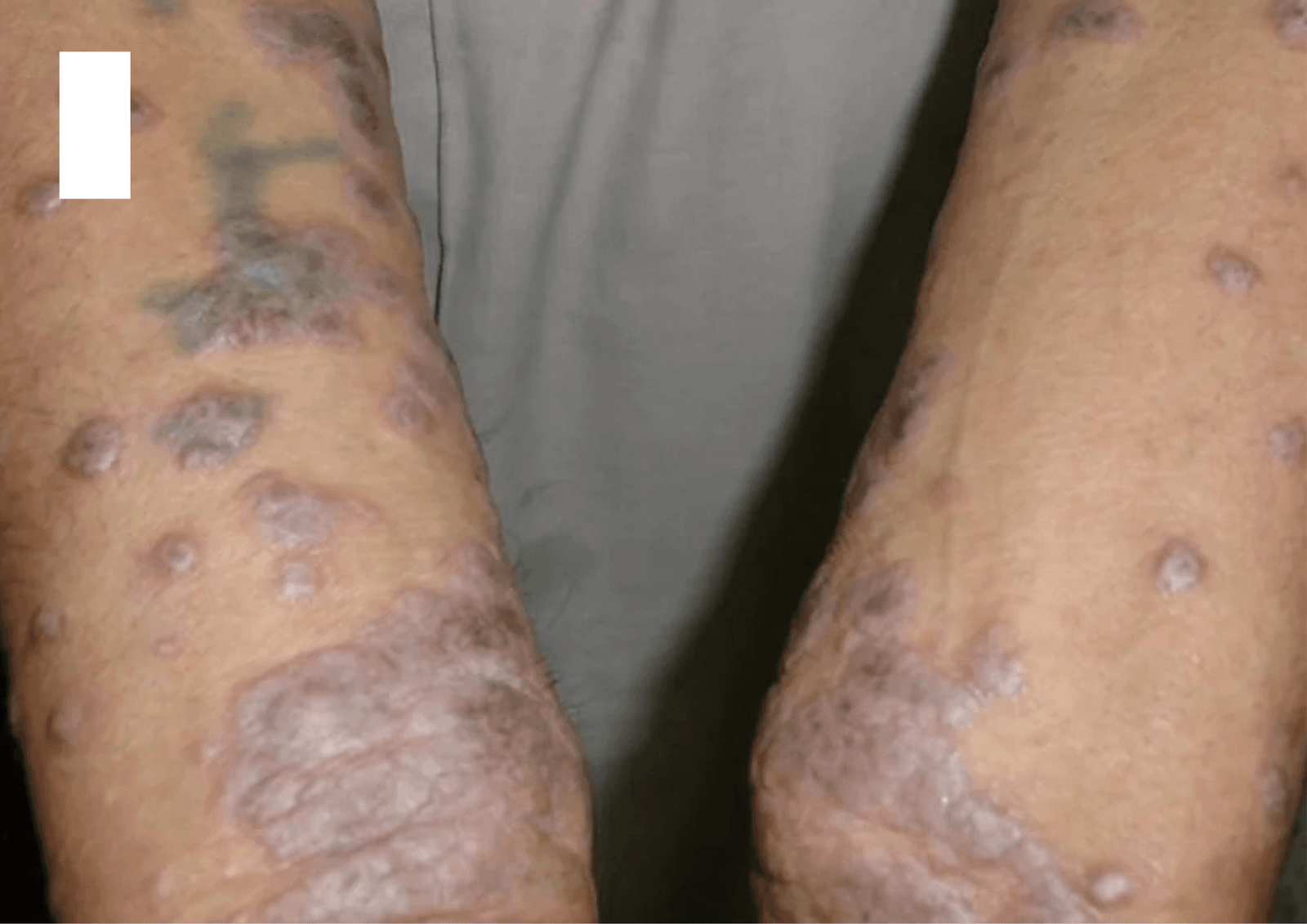
Signs and symptoms of autoimmune disease :
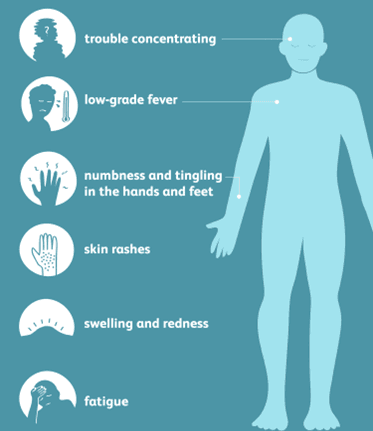
Autoimmune diseases can have a wide range of symptoms, as they affect various parts of the body Typical signs and symptoms include:
- Fatigue: Chronic state of exhaustion that does not go away with rest.
- Joint Swelling and discomfort: Inflammation of the joints can cause discomfort and restrict range of motion.
- Muscle Weakness: A generalized sense of diminished strength or weakness.
- Skin problems include redness, rashes, and other skin abnormalities like those caused by psoriasis or lupus.
- Fever: Low-grade fevers that can occur intermittently.
- Digestive Issues: Signs of diseases like celiac disease, such as bloating, diarrhea, or stomach pain.
- Nerve involvement is indicated by numbness or tingling, which is frequently felt in the hands or feet.
- Hair Loss: Patches of hair loss or thinning hair (alopecia areata, for example).
- Swollen Lymph Nodes: Immune response-induced enlargement of the lymph nodes.
- Challenge Focusing: Sometimes called “brain fog.”
Ayurvedic treatment emphasizes reestablishing equilibrium through dietary adjustments, herbal treatments, detoxification (Panchakarma), and lifestyle changes. Ayurvedic Approaches to Autoimmune Disorders
1.Dietary Changes:
Anti-Inflammatory Foods: Give special attention to fresh produce, whole grains, and healthy fats. Ginger, garlic, and turmeric are all great anti-inflammatory foods.
Steer clear of trigger foods: For some people, processed foods, sweets, and dairy might exacerbate autoimmune symptoms.
2.Herbal Treatments:
Ashwagandha:

This adaptogenic herb boosts immunity and protects against stress.
Guggulu:

Known for its ability to reduce inflammation, guggulu can aid in the management of symptoms related to a number of autoimmune diseases.
Brahmi:

This herb promotes mental clarity by lowering stress and supporting cognitive function.
3.Lifestyle Modifications:
Stress Management: Techniques like yoga, meditation, and mindfulness can help lower stress and bring the body back into balance.
Regular Exercise: Maintaining a healthy weight and enhancing circulation are two benefits of regular, mild exercise that promotes general health.
4.Detoxification:
Panchakarma: This Ayurvedic detoxification procedure includes treatments meant to get rid of toxins and bring things back into harmony. To learn more about this option, speak with a trained professional.
5.Emotional Well-Being:
Mental Health Practices: It is essential to address emotional aspects. Resilience and mental health can be enhanced by journaling, therapy, or artistic endeavors.
Get More Information Click Here.
If you are want 1oo % ayurvedic medicine Click Here.